この記事では、Windowsで使用する外付けストレージ・デバイスのパフォーマンスを向上させる方法をご紹介します。
デバイスのパフォーマンスを向上させる方法は以下のようにいくつかあります。
- システムリソースのチェック
- ハードウェア設定で書込みキャッシングを有効にする
- Windowsのネイティブ・ファイル・システムであるデバイスのNTFSをフォーマットする
注:書込みキャッシングを有効にすると、選択したフォーマットに関係なくデバイスの速度がアップします。
システムリソースのチェック:
大容量データを転送したい場合や転送の全般的な速度を高めたい場合は、他の作業を最小限に抑えることが大切です。そうすることで、システムがデータ転送により集中することができ、パフォーマンスが向上します。
書き込みキャッシングとは?
書き込みキャッシングは、揮発性メモリ (RAM) を使用してストレージ・デバイスに送信される書き込みコマンドを収集することでパフォーマンスを向上させるものです。これらのコマンドをキャッシングすることで、コンピュータはそれらが外付けストレージ・デバイスに書き込まれるまで一時的に保存できるようになります。
書き込みキャッシングはパフォーマンスを向上させるものですが、注意しなければならない点もいくつかあります。停電、ハードウェアの故障、あるいはデバイスを安全に取り外さなかったなどという理由で、RAMに残っていたデータが外付けストレージ・デバイスに書き込まれないことがあります。そのような状況により発生するデータロスやデータ破損に注意しなければなりません。詳しくは、リンク先のMicrosoftの記事をご覧ください。
注:外付けストレージ・デバイスは、安全にコンピュータから取り外すことが非常に重要です。安全な取り外しの手順は以下の通りです。
Windowsで書き込みキャッシングを有効にする方法:
- 外付けストレージ・デバイスをコンピュータに接続します。
- [マイコンピュータ] または [このPC] を右クリックして、[管理] をクリックします。
- [デバイスマネージャ] を選択します。
- [ディスクドライブ] を開きます。
- ディスク書き込みキャッシングをオンまたはオフにしたいドライブを右クリックして、[プロパティ] をクリックします。
- [ポリシー] のタブをクリックします。
- [高パフォーマンス] をクリックして選択します。
- [デバイスの書き込みキャッシュを有効にする] をクリックして選択します。
- [OK] をクリックします。

外付けストレージ・デバイスの安全な取り外し方:
- Windowsシステム・トレイの [安全な取り外し] アイコンをクリックして、取り外すことができるデバイスを表示します。
| Windows 7 | Windows 8/Windows 10 |
 |  |
- [ハードウェアの安全な取り外し] アイコンが見つからない場合、システム・トレイの [隠れているインジケーターを表示します] の矢印をクリックして通知エリアのすべてのアイコンを表示してください。
- デバイス一覧から、取り外したいデバイスを選択します。デバイスを安全に取り外すことができるようになると、Windowsが通知を表示します。
- コンピュータからハードディスク・ドライブを取り外します。
デバイスをNTFSにフォーマットすることで行うパフォーマンスの最適化
ストレージ・デバイスの中には、MacにもWindowsにも対応できるように予めexFATにフォーマットされているものがあります。Windowsコンピュータのみでドライブをご使用になる場合は、ドライブをNTFSにフォーマットすることでファイルコピーのパフォーマンスを最適化することができます。
ファイルシステムの選択
以下の場合はNTFSを使用:
ストレージ・デバイスはWindowsコンピュータに接続するだけで、Macでストレージ・デバイスに書き込みを行わない場合。
以下の場合はexFATを使用:
MacとWindowsの両方でストレージ・デバイスの読み書きを行う必要がある場合。
デバイスのフォーマット方法:
- ストレージ・デバイスが、コンピュータに接続され、マウントされていることを確認してください。
- [検索]を開き、「Disk Management」と入力します。検索結果で [ディスク管理] をダブルクリックします。
- [ディスク管理] ウィンドウの中央に表示されるストレージ・デバイスの一覧から、該当する外付けストレージ・デバイスを探します。
- フォーマットにはパーティションが必要です。フォーマット済みの場合、パーティションを右クリックして、[削除] を選択します。
- 新しいパーティションを作成するには、ボリュームを右クリックして、[新規シンプルボリューム] を選択します。[新規シンプルボリューム] ウィザードが表示されたら、画面上の指示に従います。
注:お使いのデバイスで書込みキャッシュが有効化されている場合は、クイックフォーマットを実行する際にexFATファイル・システムを使うことができません。以下をご参照ください:
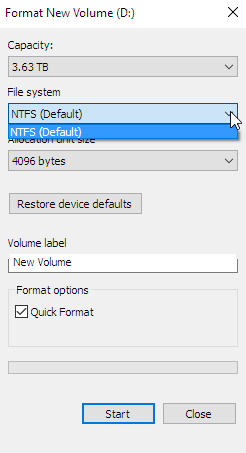
このような場合、再度exFATをフォーマットするには、[ディスク管理] でそのボリュームを削除して、画面の指示に従ってドライブをexFATにフォーマットする必要があります。
その他の方法については、ハードディスク・ドライブのフォーマット方法をご覧ください。





