Building for Multiple Architectures
We have covered in the Getting Started and
Understanding Apps sections how to build an app, without
specifying the target architecture. This means the architecture of the system
used to build the app is assumed, in most cases x86_64.
This is useful for testing the app inside the NAS OS VM, or building for
x86_64 NAS devices. But there are devices with other architectures.
Note
See Supported Architectures and Toolchains and Supported Devices for the list of supported architectures and devices.
To build an app for other architectures, you have one of the following options:
We will present both methods, and then give some details on Multi-Arch Considerations inside the NASOS SDK.
Specifying the Target Architecture
Using the Graphical Tool
New in SDK 0.7
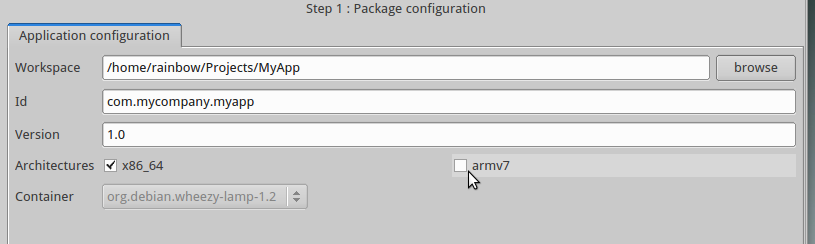
When using the SDK, with the NAS OS SDK graphical tool, the target architecture
is specified in the project configuration window. Select
Edit\Update configuration and then choose the desired architecture in the
Architecture field:
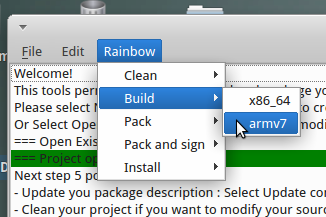
You can then select the architecture while building:
Using the Command Line
With the command line, you need to specify the --arch option to the --build
and --pack commands, such as:
sudo rainbow --build <directory> --arch=<architecture>
and:
sudo rainbow --pack <directory> --arch=<architecture>
Note
When omitted, the --arch value is assumed to be the one of the system
used to build the app.
Multi-Arch Considerations
Cross Compiling
When the app requires compilation, it has to be cross compiled. This part is actually not handled by the NASOS SDK itself, and has to be performed separately.
If your app requires cross compilation, you can refer to the Cross Compilation Reference section for help on how to generate the binaries for the target architectures.
Once you have you binaries, we recommend copying them to the source directory
of your project, preferably with a sub-directory per architecture.
Then, from the build.sh script, install the binaries at the appropriate
location. You will be able to determine the target architecture using the
$RAINBOW_ARCHITECTURE environment variable.
Here is how such a build.sh script would look like
#!/bin/bash mkdir -p /opt/my_app/bin install -m 755 /home/source/$RAINBOW_ARCHITECTURE/my_app_daemon /opt/my_app/bin
Note
It’s important to understand that the NASOS SDK doesn’t perform the cross compilation itself. For the NASOS SDK, “building” and app means “putting the app together” and no compilation is involved.
Build Directory
As seen earlier in this documentation, all the files generated during the
app’s build process are located in the build directory of the project.
Inside this directory, a sub-directory for the build’s architecture is created.
This means, while building for x86_64, the build directory will be
build/x86_64, and for armv7 it will be build/armv7.
The generated package will always be found at:
build/<architecture>/<package_id>-<version>-<architecture>.rbw
Architecture Specific Settings
As seen before, the architecture allows
specifying the package’s architecture. For a single architecture app, this
should be in the app’s package.json. For a multi-arch app, it’s best not to
specify it in package.json. The package’s architecture value will be decided
when building/packaging the app (see above).
It’s possible to have some arch-specific settings by writing a file named:
package-<arch>.json
If such a file exists, when building/packaging the app for this architecture,
the settings specified there will override those from the main package.json.
It’s also possible to add new, custom settings, for example by using the
settings property.
Building for a Foreign Arch
When building inside the NASOS SDK VM for an architecture other than x86_64
(namely armv7), most of the building process is run using the qemu machine
emulator. This means that:
- The build process can be much slower
- Some operations can fail with ‘unsupported instruction’ errors
- Some programs might behave differently than when running on an actual device
In most cases though, this leads to a succesful build. When it not the case, we recommend using an actual NAS device to build the app (see Building from a NAS Device).
Building from a NAS Device
When the qemu emulation isn’t working, or for any other issues with building
the app inside the SDK, it’s possible to use an actual device.
Building from a NAS device is in fact done exactly as inside the NASOS SDK VM,
using the rainbow command line utility.
The dependencies for the app must be installed first. To install them,
you can use the App Manager interface or the rainbow utility. Please refer
to the debugging for more details.
You will find the list of availables containers here.
Then you will need to copy the app project on the device, using e.g. scp or
rsync. For this, you will first have to
enable SSH on the device.
You could for example do:
scp -r <project_dir> admin@<nas_ip>:/tmp
Then, connect using ssh:
ssh admin@<nas_ip>
And, from the NAS:
sudo rainbow --install <container>.rbw cd /tmp/<project_dir> sudo rainbow --build . sudo rainbow --pack .
The resulting package will be found in
/tmp/<project_dir>/build/<arch>/<package_id>-<version>-<arch>.rbw
Then refer to the debug section for instructions on how to install and test the app.
In the next section, you’ll learn how to publish your app once it’s finished.